The window is a model that tries to explain how a new idea is accepted by a given society based on its current state of its already accepted political ideas. The window is meant to predict the acceptability of certain political ideas, though some politicians have tried to use it to get their idea to be accepted by their society. Unfortunately for them, this misses the entire point of the Overton Window. This is because the Overton Window is not a model for how policies get accepted, but why they do. It's a little hard to describe but I'll try to do my best to have it make the most sense. In case you're still confused by the end of the reading, I found a video by Joseph Lehman himself, of the innovative man describing the Overton Window in his own words.
Going on a scale from "More Freedom" to "Less Freedom" The position of the window on the graph is based on the amount of freedom that a certain society has been given. If there is more freedom given to a certain society, than more radically free-thinking ideas are projected to be accepted by that society. On the other side, if there is much less freedom in a society, that society is much more likely to adopt ideas that coincide with their ideas of limited freedom for the people. Because of this, ideas that are in the window in one society may not be in the window for another society. Time is also a huge factor in determining the position of the window because policies and public perception are always changing over time no matter what society you are talking about.
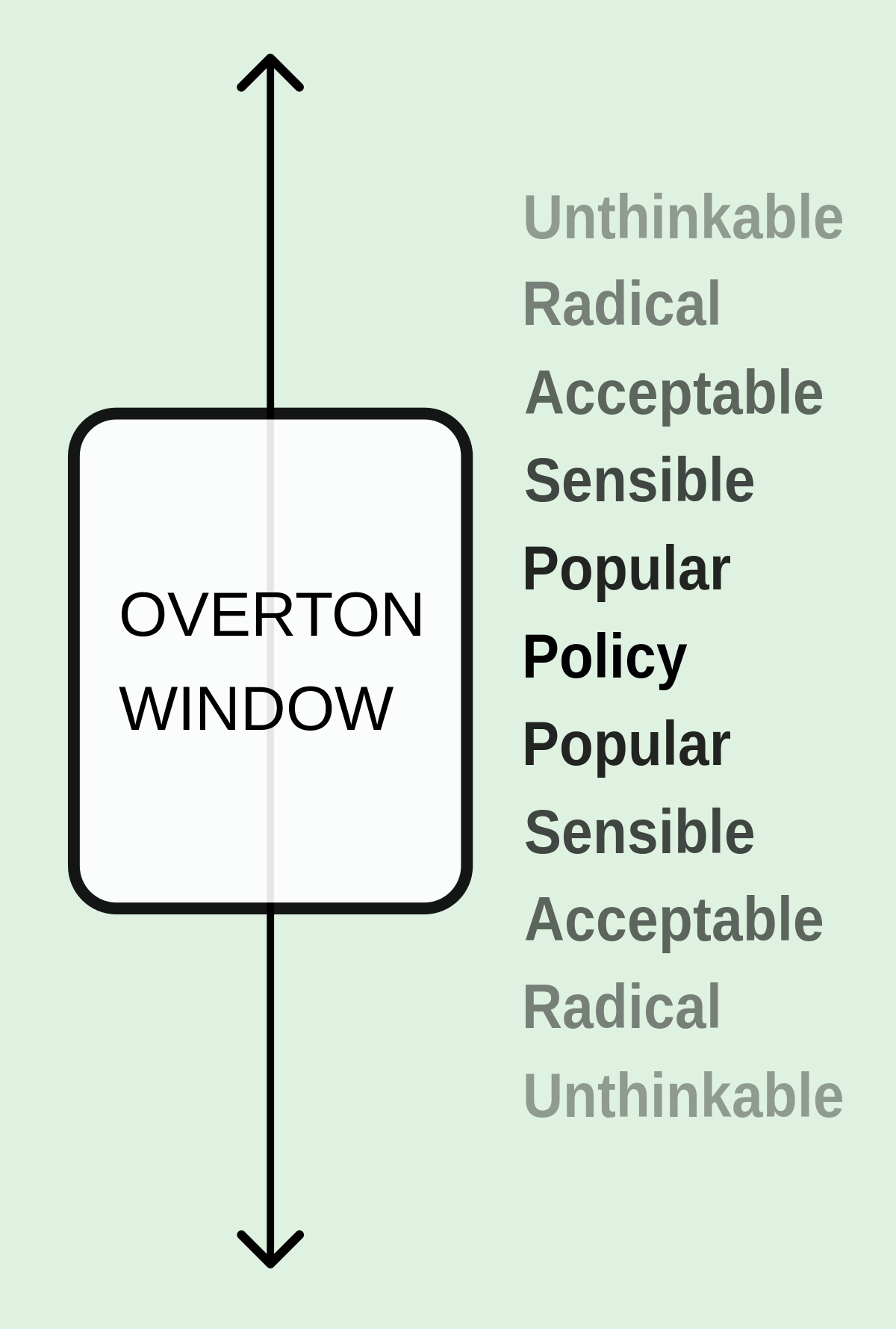
There are 6 levels to each side of the model to help further categorize where a certain idea might be in relation to the window. These 6 levels spread out to each end of the scale and go from being considered "policy" right in the middle, down to "popular," then "sensible," followed by "acceptable," "radical," and "unthinkable." Ideas in the "policy" category are very likely to be made into policy, or already are, in that given society. On the other hand, ideas that are found in the "unthinkable" range, are ideas in which that society has no chance of accepting at the given time frame.
One good example for showing how the Overton Window works is the topic of gay marriage. Back in the 1950s, gay marriage would've been found somewhere in the radical or unthinkable range of ideas for American Society in that day. Flash forward to 2021, and we find this topic to be in the category of "policy" at this point. This shows just how easily the Overton Window can change, and how quickly different policies can shift into different categories in this model. Although it can be volatile at times, the Overton Window is a very useful tool for showing the position of where a certain idea stands in relation to its society.



No comments:
Post a Comment